The GST is a destination/consumption based tax system in which the tax is levied during the supply of the taxable goods and/or services. Now, the type of supply decides a lot of things in GST, including whether the supply is taxable or not, the rate of GST, etc.
Contents [Hide]
Definition of Supply Under GST
In order to understand the rules and definition of supply GST act, we must first know what a supply is. A ‘Supply’ refers to the purchase, import, sale, exchange, transfer, rental, barter, license, lease or disposal of goods and/or services made by a person through his/her business.
Time of Supply in GST
The time of supply under GST is the point in time when the particular goods and/or services were supplied or deemed to be supplied to the recipient. The rate of GST, taxable value, and due date are determined based on the time of supply. Under GST, the taxes are liable to be paid at the time of supply.
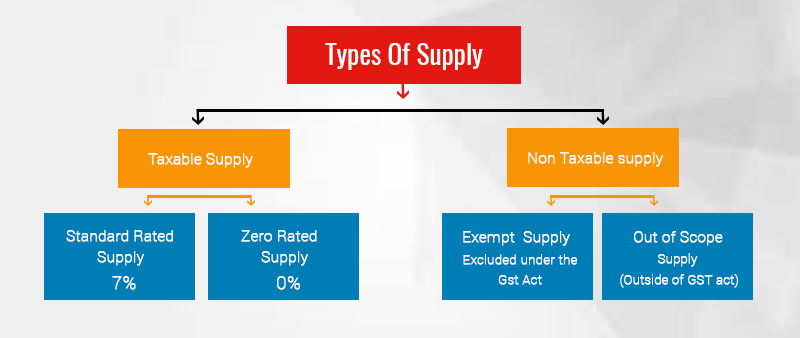
Types of Supply in GST
A ‘supply’ can be of various types depending on the time of supply, place of supply, type of commodities, the recipient and the seller, and the tax liability. Let’s figure out the difference.
Recommended: Simple Ways to Determine the Supply of Goods and Services
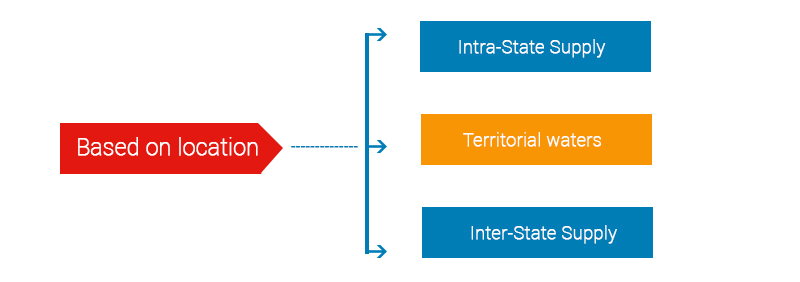
Location based (Place of supply)
There are three types of supplies in this category – interstate supply, intrastate supply, and territorial waters supply.
Place of supply of goods under GST with examples
Intra-state supply includes the supplies of goods and/or services where both the supplier and the recipient (place of supply) are in the same State or UT, except the supplies made from/to a SEZ unit or SEZ developer, imports of goods, and the supplies made to a tourist.
Example: Mr. Arjun of Jaipur, Rajasthan sells 50 laptops to Mr. Nikhil of Jaipur, Rajasthan.
In this case, the place of supply is same to CGST and SGST will be charged.
Inter-state supply includes all those supplies where the supplier and the recipient (place of supply) are in two different states or UTs or in a State and a UT.
Example: Mr. Arjun of Jaipur, Rajasthan sells 50 laptops to Mr. Nikhil of Mumbai, Maharashtra.
In this case, the place of supply Mumbai, Maharashtra. So IGST will be applied.
Interstate supplies also include the following:
- The imports of goods/services into the Indian Territory
- Supply from India to an outside place.
- Supplies from/to a SEZ unit or SEZ developer
Territorial Waters supply includes the supplies where either or both the location of the supplier and the place of supply are in the territorial waters.
Place of supply rules GST India
GST has the provision of Central GST, Integrated GST, and State GST taxes depending on the location (place) of the supply. The CGST and SGST will be levied on all the intra-state supplies, while IGST will be levied on all the inter-state supplies. The supplies made from/to a Union Territory will be liable for UTGST which is same as State GST.
Download GST Valuation Rules in PDF
Combination based (Products to Supply)
Composite supply: The supply of two or more taxable items under the same supply or combination of supplies are counted as Composite supplies, where one of the supplies is a principal supply.
Mixed supply: When two or more individual supplies are made in conjunction for the same price by a single person but doesn’t count as a composite supply.
Continuous supply: It is further categorized into two:
- The continuous supply of goods are the supplies made on a continuous basis for which the recipient gets regular invoices from the supplier.
- The continuous supply of services are the supplies made on a continuous or recurrent basis, for minimum three months, with monthly or other periodic payments.
Recipient based (Direction of Supply)
There are two types of supplies in this – Inward supply and Outward supply.
Inward supply is the purchase/acquisition or any other kind of receipt of goods or services with or without a payment.
Outward supplies include the supply of good and/or services in the form of sale, transfer, lease, rental, exchange, barter or disposal, usually in a business.
Tax based (GST on Supply)
Based on tax liability, the supplies are divided into the following types:
Tax exempt supply: The supplies which attract nil rate under GST or the ones which are free of tax are called tax exempt supplies. This also includes non-taxable supplies. A taxable person is not required to pay GST on such supplies.
Zero-rated supply: The exports of goods/services and supply of commodities to/from a SEZ developer or a SEZ unit are zero-rated supplies under GST.
Taxable supply: Supplies which are liable to pay tax under GST.
Non-taxable supply: It is similar to the tax exempt supply and attracts nil rate GST tax.
Depending on the type of supply, different GST rates are applicable on different commodities under the GST tax regime.