An invoice is a prime tool used by the government to assess and calculate the valid taxes being imposed on the taxpayers. The invoice is ascertained on the goods and service provided by the seller and is noted down in the tax file for future reference in the tax department. But the goods and service tax in India is a latest and revised format for invoicing which will facilitate the overall computation and eligibility of tax on all the invoiced goods and services.
The government authority has issued two types of the invoice which must be furnished by the taxpaying entity of business unit with should be up to date with the compliance. Tax invoice and bill of supply are the two newly issued bill format which are further explained in detail:
Contents
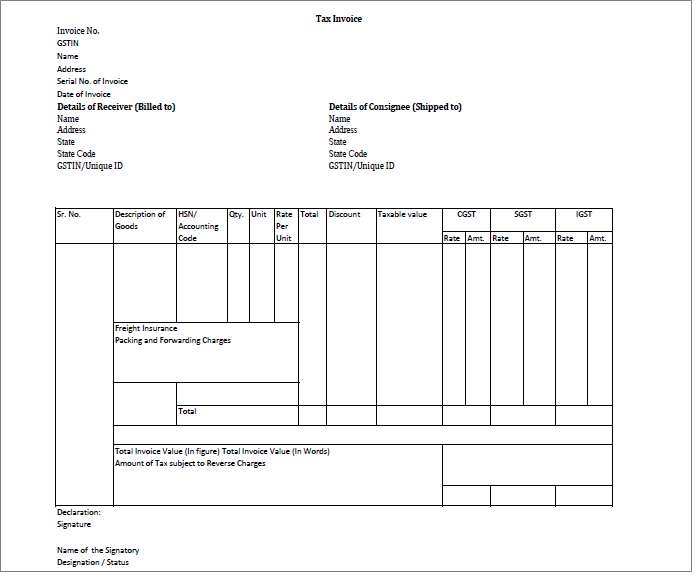
Tax Invoice
Every registered supplier of goods and services must issue a tax invoice whenever there is a supply of taxable goods and services. Some of the strict and rules and regulation are given to be followed while using the invoice at the time of issuing:
- A serial number of the invoice which is consecutive and consist of letters, numbers, special characters, or any combination respectively and are also unique for each and every financial year.
- Another is stated name and code attached and are required if the recipient of goods/services is unregistered and the taxable value of goods or services supplied is Rs. 50,000 or more while for interstate supply, the state’s name and code are compulsory.
- GSTN/unique ID: A GST identification number is necessary for the receiver as there are different codes for UN bodies, embassies, or any other class of persons being included.
- HSN code/accounting code: The concerned entity compulsorily add an HSN code for the goods and an accounting code for the services supplied.
Bill of Supply
The bill of supply will be issued by the registered supplier in two cases, as when the goods and services are exempted and when the supplier chooses to pay the taxes under the composition scheme.
Going through the rulebook of the government authority by the bill of supply is governed:
1. Serial number – The serial number must be a consecutive number having letters and/or numbers and must be unique for the individual financial year.
2. Details of receiver: It requires the name, address, and GSTIN/unique ID of the receiver only in the case when the receiver is registered.
3. Particulars of goods: For the supplied value of goods or services, the term “value” is used instead of “taxable value,” as in the tax invoice.
In the case of any product or service costing below 100 rupees need not generate any bill of supply but can maintain the bill of supply in a consolidated format which can be used for further usage.
There are certain time limits imposed by the government of India on the issuance of the invoice. The conditions are mentioned below:
Supply of goods:
Where supply includes the movement of goods, the registered person must issue an invoice before or at the time goods are removed for supply. While in another scenario, the invoice should be issued before or at the time goods are delivered or provided to the customer.
Supply of services:
The concerned tax invoice must be issued within 30 days from the date of supply of services unless the transaction involves banks or other financial institutions, in that case, the invoice must be issued within 45 days.
Receipt voucher:
A receipt voucher or other relevant documents must be issued as an advance receipt on the supply of goods or services.
Reverse charge mechanism:
If goods and services are supplied by an unregistered person, the registered receiver should issue an invoice on the date of receipt of goods or services. In this, the recipient, not the supplier, is liable for the tax.
A continuous supply of goods:
When goods and services are supplied – and payment is made – periodically, the registered supplier must issue an invoice along with each statement or payment.
If in case, one has to revise or change the taxable value or the GST chargeable on the invoice which has been already issued, the entity has to issue a debit or credit note based upon the transactions.
Credit note is issued when the taxable value and/or GST charged on the invoice is needed to be reduced
Debit note is issued when the taxable value and/or GST charged on the invoice is needed to be increased.
While credit notes are circulated on a more vigilant basis i.e. a credit note concerned with an invoice of a financial year can be issued before September 30 after the end of the financial year or the date of filing of the relevant annual return, whichever is earlier.
Invoice bearing signature
The invoice must be signed by the registered individual or by the authorized executive of the concerned registered individual while the sign can be either digital via Digital Signature Certificate or by physically, any means preferable according to the feasibility. Also, every invoice must be strictly according to the format and under the framed rules in order to avoid the penalties of noncompliance.
For more details regarding the GST India, Please download our GST helpline mobile application that is available on both iOS and Android platforms. The GST app comes with very smooth UI design and is also available for use in both online and offline modes.
Understood The Process of Invoicing under GST Regime in India? Do share your views and thoughts if you have any issue.
Don’t miss any information about GST ! Download GST App today to get the latest updates. Thank you!